Tête penchée
en avant sur un écran
Maux de tête liés à l’exposition aux écrans
Notre consommation d’écran augmente !
Le temps passé devant des écrans a augmenté de
50% depuis 2009(1)


Activation des points
de tension
dans les muscles
du dos, de la nuque
et du crâne (2-4)

Transmission
de la douleur
au cerveau (2-4)

Hypersensibilisation
du cerveau
à la douleur (2-7)
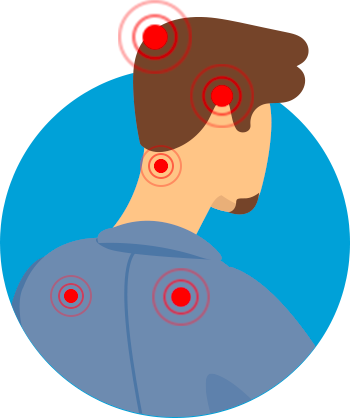
Augmentation de
la fréquence et de
l’intensité des céphalées
de tension (2-7)
1 - https://www.statista.com/chart/9761/daily-tv-and-internet-consumption-worldwide
2 - Fernández-de-Las-Peñas C et al. (2007) Myofascial trigger points, neck mobility, and forward head posture in episodic tension-type headache. Headache. 47:662-672.
3 - Fernández-de-Las-Peñas C et al. (2011) Referred pain from myofascial trigger points in head and neck–shoulder muscles reproduces head pain features in children with chronic tension type headache. J Headache Pain. 12:35-43.
4 - Palacios-Ceña M et al. (2017). Relationship of active trigger points with related disability and anxiety in people with tension-type headache. Medicine (Baltimore). 96:13(e6548).
5 - Matsuda M et al. (2019) Roles of inflammation, neurogenic inflammation, and neuroinflammation in pain. J Anesth. 33:13113-9.
6 - Lee E et al. (2019) Impact of cervical sensory feedback for forward head posture on headache severity and physiological factors in patients with tension-type headache: a randomized, single-blind, controlled trial. Med Sci Monit. 25:9572-9584.
7 - Castien RF et al. (2018) Pressure pain thresholds over the cranio-cervical region in headache: a systematic review and meta-analysis, J Headache Pain. 19:9.
7000031487-12/20
